Power Screw -
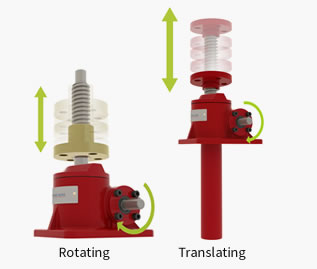
Power screw is a mechanical device which is used to convert rotary (turning) motion into to the translational (linear) motion. It is used as a linkage in a machine. Linkage is a assembly or a network of rigid linkages used to manage forces and moments. It uses helical motion of screw to transmit the power.
Main applications of power screw
1) used to raise the load eg. Screw Jack
2) to obtain accurate motion e.g.Lead Screw of lathe
3) to load a specimen on UTM [Universal Testing Machine]
4) to clamp a workpiece e.g.vice
Advantages of power screw :-
Types of power screw [on basis of threads or forms of threads] :-
Power Screws are classified on the basis of geometry of their threads.
{Note:- 'Power screws' and 'Fasteners' both have threads. V shaped threads are commonly used in fasteners as their function is to join two objects 'non permanently'. V threads provide friction to minimise the chances of loosening. V threads are exact opposite of threads used in power screws. Threads in power screw provide low friction between nut and bolt so as to transmit power.
Types of threads commonly used in power screw :-
1) Square
2) ACME
3) Trapezoidal
4) Buttress thread
1] Square Thread:-


2] ACME Thread :-

3] Trapezoidal thread

4] Buttress thread


Parts of Power Screw:-
➡ screw
➡ nut
➡ a part which hold either nut or bolt in respective place.
Motion in two way:-
1) Screw moves in axial direction and nut kept stationary.
e.g. screw jack and vice
2) Nut moves in axial direction and screw kept stationary.
eg . Lead screw of lathe machine
This was basics about power screw.
Screw Jack:-




Power screw is a mechanical device which is used to convert rotary (turning) motion into to the translational (linear) motion. It is used as a linkage in a machine. Linkage is a assembly or a network of rigid linkages used to manage forces and moments. It uses helical motion of screw to transmit the power.

Main applications of power screw
1) used to raise the load eg. Screw Jack
2) to obtain accurate motion e.g.Lead Screw of lathe
3) to load a specimen on UTM [Universal Testing Machine]
4) to clamp a workpiece e.g.vice
Advantages of power screw :-
- It has large load carrying capacity
- It has small dimensions and easy to design n manufacture
- Highly accurate translational motion
- Minimal number of parts engaged in this device
- Poor efficiency due to two large frictional losses
- Due to high friction; rate of wearing is high
Types of power screw [on basis of threads or forms of threads] :-
Power Screws are classified on the basis of geometry of their threads.
{Note:- 'Power screws' and 'Fasteners' both have threads. V shaped threads are commonly used in fasteners as their function is to join two objects 'non permanently'. V threads provide friction to minimise the chances of loosening. V threads are exact opposite of threads used in power screws. Threads in power screw provide low friction between nut and bolt so as to transmit power.
Types of threads commonly used in power screw :-
1) Square
2) ACME
3) Trapezoidal
4) Buttress thread
1] Square Thread:-


- They have much higher efficiency and lowest friction.
- They are hard to manufacture and difficult in machining.
- Due to ZERO degree thread angle, there is no radial pressure or bursting pressure on Nut. This increases nut life.
- used in high load applications such as screw Jack, clamping device.
- It has less thread thickness than other types.
- It's not possible to use split type nut in this case [Split nut is that which can split into two equal halves so that it can be positioned on a shaft or belt]
2] ACME Thread :-

- It has 29 degree thread angle
- Strength of screw depends upon thread thickness of core diameter. ACME and trapezoidal threads are stronger than square threads due to more thread thickness
- Due to presence of thread angle, nut is subjected to radial or bursting pressure and hence efficiency is less than square threads.
- Split type nuts can be used here
- These threads are used in lead screw and other power transmission devices.
3] Trapezoidal thread
- ACME and trapezoidal screws are mostly similar except the thread angle.
- Trapezoidal thread angle is 30 degree while ACME thread angle is 29 degree.
- Uses same as ACME.
4] Buttress thread
- They are designed such that force or load is applied only in one direction.
- Strongest thread as it has largest thread thickness
- Easy to manufacture and comparable efficiency with square screws.
- Used in light Jack screw and vices.
Parts of Power Screw:-
➡ screw
➡ nut
➡ a part which hold either nut or bolt in respective place.
Motion in two way:-
1) Screw moves in axial direction and nut kept stationary.
e.g. screw jack and vice
2) Nut moves in axial direction and screw kept stationary.
eg . Lead screw of lathe machine
This was basics about power screw.
Screw Jack:-

- Screw Jack is a special case of power screw which raises or lowers the load by applying a small force in the horizontal plane.
- Screw thread is nothing but helical grows which are cut by either left or right hand mainly used to lift heavy weights.
- Screws which are tightened in clockwise direction term as right hand thread, screws with left hand threads are used exceptionally.